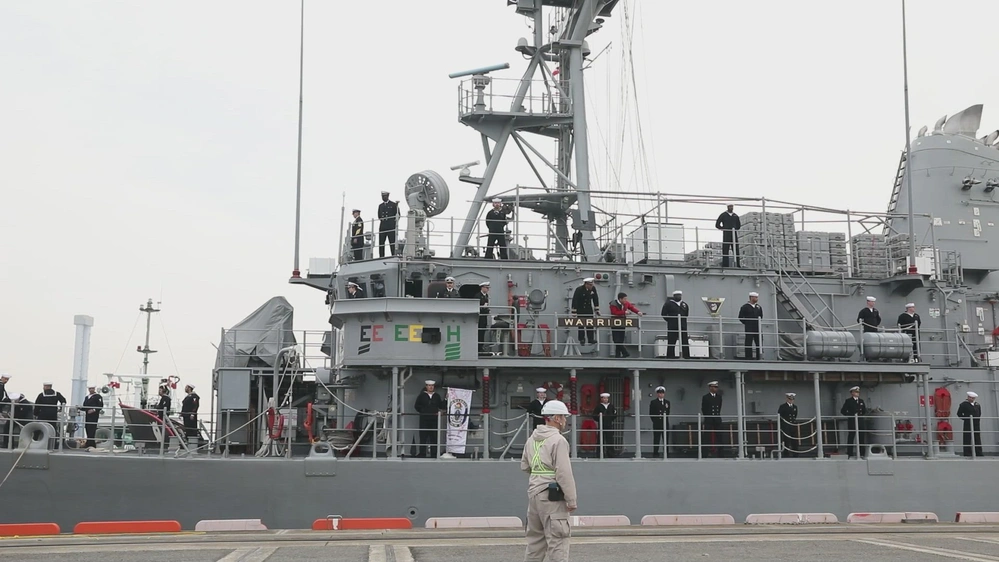
The USS Warrior, a mine countermeasures ship of the United States Navy, made a port visit to Kobe, Japan, as part of its ongoing deployment in the Indo-Pacific region. The visit highlights the strong ties between the U.S. and Japan, emphasizing their commitment to regional security and cooperation.
During its stay in Kobe, the crew engaged in community outreach activities, participated in cultural exchanges, and hosted tours of the ship for local residents, fostering goodwill and mutual understanding. The visit also provided an opportunity for the crew to experience Japanese culture and strengthen relationships with their Japanese counterparts.
The USS Warrior’s presence in Kobe underlines the importance of naval partnerships and the shared values of peace, stability, and prosperity in the region. This visit is part of a broader effort to enhance maritime collaboration and ensure a free and open Indo-Pacific.
Warrior, commanded by Lt. Cmdr. Raymond V. Piana, is an Avenger Class mine countermeasures ship. The ship is approximately 68 meters long and displaces approximately 1,250 tons with a crew size of about over 90.
Mine countermeasures ships, such as Warrior, play a critical role in maintaining maritime security by locating, identifying, and neutralizing underwater mines, thereby ensuring safe passage for naval and commercial vessels.
Sailors are excited to visit Kobe to experience the wonderful culture, history and sights that the city offers while being involved in community relations opportunities.
The U.S.-Japan alliance has long been the cornerstone of regional peace and security in the Indo-Pacific region.