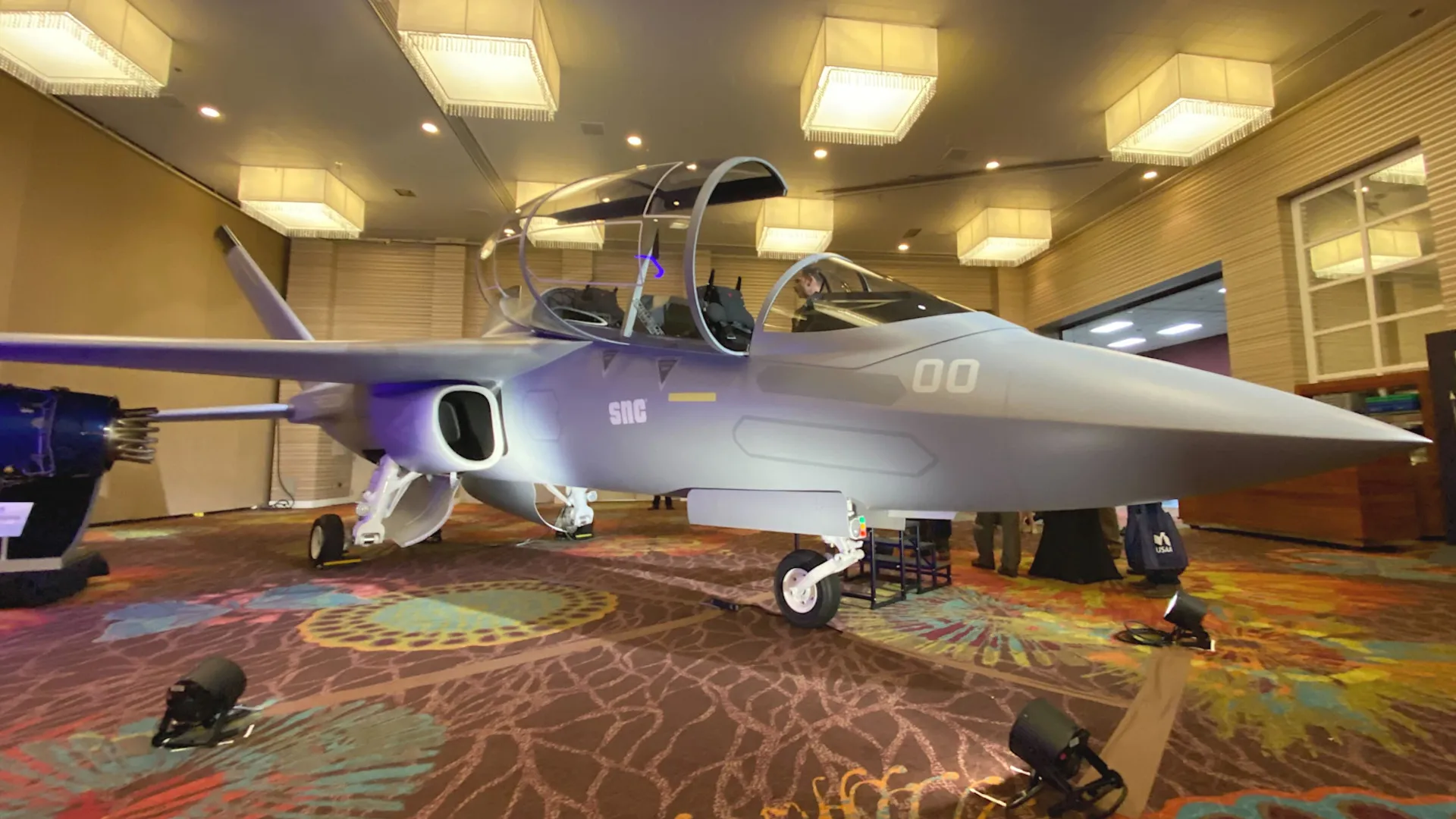
The Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC) has rolled out a new pitch for a successor to the Navy’s T-45 Goshawk jet trainers. Interestingly, SNC’s proposal focuses heavily on the ability of its clean-sheet twin-engined Freedom jet design to meet certain carrier training requirements that the Navy has axed from its T-45 replacement plans.
SNC made a formal announcement about putting the Freedom jet forward for the Navy’s forthcoming Undergraduate Jet Training System (UJTS) competition today, around the Tailhook Association’s main annual symposium, at which TWZ is in attendance. SNC has been working on the Freedom design in cooperation with Turkish Aerospace Industries (TAI, and also abbreviated TUSAS in Turkish) for years now. Freedom was previously presented as a contender for the U.S. Force’s T-X trainer requirements, a competition Boeing won with what became the T-7A Redhawk. SNC has also teased the aircraft as a possible T-45 replacement in the past. TAI is not mentioned in the current pitch to the Navy.
The Navy currently has just under 200 T-45Cs in service, which are used to train future Navy and Marine aviators. The original T-45A variant, a carrier-based derivative of the British Aerospace (subsequently BAE Systems) Hawk jet trainer, began entering Navy service in 1991. The C model fleet includes a mixture of new-production and upgraded A-model jets with new avionics and glass cockpits. Other upgrades have been added to the jets over the years, as well. A proposed land-based T-45B was never produced.

“SNC’s Freedom Family of Training Systems” is “the only training aircraft capable of carrier touch-and-go and Field Carrier Landing Practice (FCLP) to touchdown with a 16,000 hour airframe life,” a product card handed out at the Tailhook Association symposium declares. “Freedom delivers uncompromising training performance and significant lifecycle cost savings for the U.S. Navy training enterprise.”
“With a focus on efficient aero performance, low lifecycle cost, FCLPs to touchdown and UNS-ownership of Digital Technical Data Package (DPP) rights, Freedom stands ready to elevate naval aviation training standards by allowing the Navy to train the way you fight – zero compromise,” it adds.
“Its innovative design and robust reliability … eliminate the need for unplanned Service Life Extension Programs (SLEP),” according to a separate press release put out today. “Further, Freedom’s US Navy-owned digital design and modular open system architecture ensures that NAVAIR controls future upgrades for the life of the UJTS program including the capability for seamless third-party system integration.”
In 2020, the Navy publicly disclosed that it was looking to axe requirements for the future UJTS aircraft to be capable of performing actual carrier landings and takeoffs. By 2023, the Navy had moved forward with that decision, but with FCLP and touch-and-go landings still part of the syllabus. Last year, it then emerged that the Navy was also looking to eliminate the FCLP requirement, cited as a key cost and schedule driver for UJTS, something that was confirmed when new requirements were publicly released in March. In the future, naval aviators may not see a carrier until they reach the Fleet Replacement Squadron (FRS) in charge of the aircraft type they have been assigned to fly.
Carrier-capable aircraft have to be designed in fundamentally different ways from their land-based counterparts, especially when it comes to the landing gear, which is typically heavily reinforced. Carrier landings are substantially harder on aircraft, overall, given the need to get down quickly in a very confined landing space that can be moving independently, coupled with the stress of catching an arrestor wire. Launch via catapult imparts additional stresses on airframes that land-based aircraft do not experience. Sustained operations at sea also require additional hardening against corrosion from saltwater exposure. All of this, in turn, can also make aircraft designed to operate from carriers more complex and expensive than similarly capable types that only need to fly from bases ashore.
Eliminating various carrier landing requirements immediately opens up a host of additional options for a new jet trainer, which could also be lower cost and lower risk. At the same time, there has already been criticism and concern for years now about the potential downstream impacts from cutting live training events from the naval aviator pipeline that cannot be fully recreated in any sort of virtualized environment.
SNC’s proposal taps into this entire debate and is presented as offering a hedge against the Navy changing course again in the future.
“It is clear to SNC that since early 2020, the Navy has been considering compromising its long-standing and important requirement to train with FCLP-to-landing,” the company told Aviation Week. “It is important to the Freedom Team that the U.S. Navy has an option to continue its essential FCLP training and avoid the unnecessary risk and cost associated with foregoing that requirement in the [Chief of Naval Air Training] syllabus.”
“As a clean-sheet design focused on the UJTS mission, the design features for FCLP-to-touchdown are minimal and affordable,” SNC further noted. “SNC believes FCLP-to-touchdown should be, at a minimum, a scored objective in the UJTS competition.”
Beyond the specifics of the Freedom design, it is certainly interesting to see a company openly buck a customer’s stated requirements. It does look set to make SNC’s proposal for UJTS distinct from the other competitors, which include a navalized version of the T-7 from Boeing, the TF-50N from Lockheed Martin and Korea Aerospace Industries (KAI), and the M-346N offered by Textron and Leonardo. The TF-50N is based on KAI’s T-50, a losing entrant in the Air Force’s T-X competition, but an increasingly popular type worldwide (including in its FA-50 light combat jet form). In July, Textron and Leonardo also unveiled a new pitch to the Navy involving the M-346N, but rebranded as a Beechcraft product. Beechcraft is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Textron.